PIP 18: Pulsar Replicator
- Status: Discarded, in favor of using Pulsar I/O connectors
- Author: Rajan Dhabalia
- Pull Request: #1582
- Discussion: https://github.com/apache/incubator-pulsar/issues/1582
Pulsar already supports geo-replication that persists messages across multiple clusters of pulsar instances. Therefore, client can set replication clusters for a topic, and pulsar broker internally takes care of replication to all the clusters. However, sometimes application may want to replicate the same published messages to other external systems which is not part of pulsar-eco system such as AWS-Kinesis, DynamoDB. Therefore, right now, client-application has to take this extra burden to publish same messages for pulsar and other external systems. Therefore, it will be useful to introduce server side replication that can replicate pulsar messages to external system without client intervention. Also server side replication should be extensible which can provide a plugin mechanism to add various replicators to support message-replication to different external systems.
- Replicate Pulsar message to external system (eg: Kinesis, Kafka, another Pulsar cluster)
- Easy onboarding: client should be able to add replicator configuration with CLI/Admin api and it should auto start appropriate replicators.
- Isolation from core message bus
- Pluggable framework and extensible to support multiple external system
- New connectors should be developed with minimal efforts
- Operability and monitoring
- API to control start and stop individual replicator
- API to get replicator stats
- Security
- Replicator framework should provide pluggable mechanism to plugin KeyStore implementation that can store and fetch client’s credentials which will be required to connect external system.
Replicator acts as a proxy that receives pulsar messages from broker and publishes to external system. In this process, replicator performs below steps:
- Create a producer that can publish messages to external system
- Receives Pulsar message for a topic
- Convert a pulsar message to appropriate format and publishes to external system.
Therefore, replicator framework should be able to accommodate various replicator providers that can create producer to replicate messages to external systems. Below is replicator provider interface which should be implemented by appropriate providers that connect to external system and replicate pulsar messages.
ReplicatorProvider.java
public interface ReplicatorProvider {
public void validateProperties(String namespace, ReplicatorPolicies replicatorPolicies) throws IllegalArgumentException;
public CompletableFuture<ReplicatorProducer> createProducerAsync(final String topic,
final ReplicatorPolicies replicatorPolicies);
}
ReplicatorProducer.java
public interface ReplicatorProducer {
void send(Message message, SendCallback callback);
}
Client can on board replicator configuration for a a namespace using admin api. It registers replicator configuration to namespace policies and auto starts replicators for appropriate topics under that namespace.
Add replicator config
Client wants to replicate published messages to specific external targeted system such as Kinesis, DynamoDB, etc. Therefore, client needs to provide metadata to replicator using which replicator can connect to external targeted system and publish messages. Below admin api adds replicator metadata config for a namespace using which replicator can connect to external system.
pulsar-admin namespaces add-repl-config <namespace>
--type Kinesis \
--region-name us-east
--replication-properties <properties> \
--auth-plugin-name org.apache.pulsar.replicator.auth.DefaultAuthParamKeyStore \
--auth-param {“accessKey”: ”test”, “secretKey”: “test”} \
--topicNameMapping {“pulsar-topic1”:”stream1:us-west1”, ”pulsar-topic2”:”stream2:us-east1” , ”pulsar-topic3”:”kinesis3:us-west2”}
type: type of replication provider eg: Kinesis, DynamoDB, etc.
region-name: region-name/cluster-name of external system
replication-properties: replicator provider specific properties
topicNameMapping pulsar topic to external-system stream name mapping
auth-plugin: FQCN of auth plugin using which replicator service can get secrets and connect to appropriate resources.
auth-param: auth-param required for Auth-plugin to store/fetch credential required to connect to external system.
Remove replicator config
Below admin api removes replicator metadata configuration for a namespace.
pulsar-admin namespaces remove-repl-config <namespace> --type Kinesis --region-name us-east
In previous section we have discussed, we can onboard replicator configuration metadata using admin api and using this metadata, replicator provider can connect to external system and start replicating pulsar messages to external system. Now, we would also like to isolate deployment of replicator providers from pulsar broker so, it can not directly impact message dispatching and publish latency by not sharing broker’s resources.
We can utilize Pulsar function to deploy replicator of a topic. We can register a pulsar function for every topic’s replicator and replicator runs as a part of a function process. When client onboards replicator metadata for a namespace using admin-api, api will store metadata and it will also register a replicator function for each configured topics for that namespace.
Replicator will be running as a process under a pulsar function which will be responsible to read messages for a configured topic from pulsar broker and replicates them to the external system. Every replicator creates a unique subscription under a topic to consume messages and replicate them to external system.
Replicator function will be a lightweight function which loads the configured replicator provider package (eg: kinesis-replicator-provider) at runtime from a configured central-location (eg: bookkeeper or classpath). Keeping replicator-provider package at central location helps to upgrade specific replicator-provider's package without updating any existing replicator’s pulsar-function.
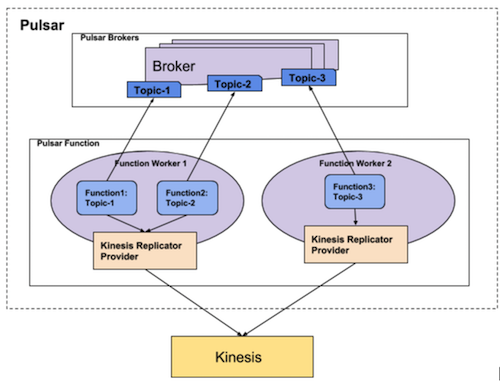
(Figure 1: Kinesis replicator on Pulsar Function)
Start/Stop Replicator
Sometimes, it requires to control message dispatching for a replicator of specific topic. So, it will be useful to provide an api which can start/stop a replicator of a specific topic.
./pulsar-admin persistent update-replicator -r Kinesis -a [Start/Stop] persistent://sample/pulsar-kinesis-namespace/replTopic
Deregister Replicator
Sometimes, client wants admin-api to deregister replicator function which should remove replicator subscription on a topic and deregister a replicator function as well.
./pulsar-admin persistent deregister-replicator -r Kinesis persistent://sample/pulsar-kinesis-namespace/replTopic
Replication service will act as a proxy to replicate messages to different targeted systems. Every broker cluster will have a peer-replicator service running on the local region. User can define replication policies at namespace so, broker can publishes pulsar messages to replicator service and replicator service will publishes to external system.
Replication-service has 2 main components :
- Replication-connectors and
- Binary proto command to replicate messages from broker to replication-service.
1. Replication connector
Replication service is a collection of various pluggable replication-connectors that talk to different external system. Replication-connector can implement replicator interfaces (discussed in replicator design) and that connector can be easily plugged into replication-service by providing FQN of the connector-class into configuration.
# Comma separated class-name for replication provider
String replicatorProviders=org.apache.replicator.KinesisReplicatorProvider,org.apache.replicator.DynamoDBReplicatorProvider
2. Binary proto command to replicate messages from broker to replication-service.
Replicator service supports following binary proto commands using which broker can connect to replication-service and sends message.
-
Connect command: Replicator service supports existing connect command so, it can authenticate broker and allow broker to connect with replicator service so, broker can send messages for replication.
-
Send Command: In pulsar geo-replication, broker uses “SEND” command to replicate messages to another cluster. Replicator service will also support “SEND” command so, broker can replicate messages similar way to replicator service as well.
There can be different options to deploy replicator service in a cluster which can be mainly differentiated based on how broker performs lookup for replicator service to connect and replicate messages to replicator-service for every topic.
1. Deploy in a cluster
Replicator service cluster will be available in every geo-location. So, pulsar broker can replicate messages to replicator service that is available on same geo-location. This option requires cluster-management to implement topic ownership among all replicator nodes registered in the service-cluster. Cluster management stores topic ownership metadata using which broker can do a topic-lookup to connect to appropriate replicator-node that owns the topic and then broker can replicate messages to that replicator-node.

2. Deploy on broker’s host
This option doesn’t include cluster-management component. In this option, replicator service will be hosted on the same host where broker service is started. Therefore, broker doesn’t require replicator service discovery but it can directly connect to local replication-service and start replicating messages to local hosted replicator. Therefore, each replication service serves topics which is owned by broker-service running on the same host.
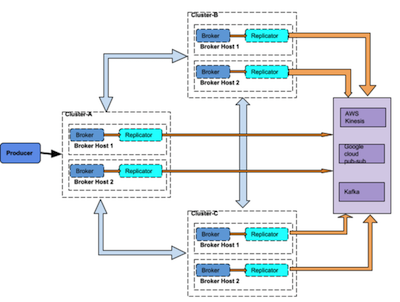
Pros:
It doesn’t require to maintain cluster-management for replication service
Cons:
Replication service has to be installed on the same host where broker service is running so, broker doesn’t have to do lookup and it can directly connect to local running replication service.
Replication service will share same host resources (eg: CPU, heap and direct memory) that is being used by broker.