A pure C# Makwa implementation with no dependencies.
Makwa was a runner up in the Password Hashing Competition, uniquely has a delegation function which allows hashing to be offloaded onto a third party server without revealing the password.
Install-Package Makwa
dotnet add package Makwa
git clone https://github.com/MitchellBerry/Makwa-Sharp.git
using Makwa;
Hasher makwa = Hasher.Create();
String password = "hunter2";
String hash = makwa.HashPassword(password);
// hash: SdVTLgfGKck_b211_TG3Uljw178dpAPtw1qILPA_JMm2w54jILdKKQMpString hash = "SdVTLgfGKck_b211_TG3Uljw178dpAPtw1qILPA_JMm2w54jILdKKQMp"
bool correct_password = makwa.VerifyPassword(password, hash)makwa.Prehashing = false;
makwa.Posthashing = 16;
makwa.Workfactor = 384;
makwa.Hashfunction = new HMACSHA512();
String hash = makwa.HashPassword(password);
// hash: SdVTLgfGKck_s307_Qh0ZKgAwQr+ieFauHFm4Vg_3B/H3xbYZZa2Ua2yfK55mAbyte[] input_bytes = new byte[87]; //[0x00, 0x00, 0x00 ...]
int output_length = 173;
byte[] kdf_output = makwa.KDF(input_bytes, output_length);byte[] salt = new byte[16]; //Use an appropriately random input, 16 bytes long
byte[] password_bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(password);
byte[] digest_bytes = makwa.Digest(password_bytes, salt);
// digest byte array, length is determined by Posthashing value| Name | Type | Effect | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
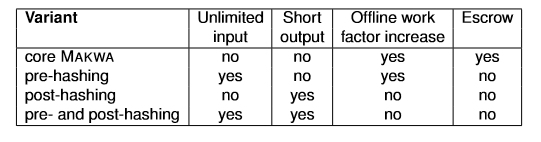
| Prehashing | bool | Hashes the input prior to the running the main Makwa algorithm. Allows an unlimited input size. | True |
| Posthashing | ushort | Hashes the result down to the specified size, the default value of 12 results in a 12 byte digest. A value of 0 applies no post-hashing and the digest will be the full size, values between 1 and 9 are not valid and will raise an exception. | 12 |
| Workfactor | uint | The number of rounds performed, a higher number will increase hashing time. Work factors are restricted to values w = x * 2y, where x = 2 or 3 and y ≥ 0, other values will raise an error suggesting the closest valid value. (See notes below) | 4096 |
| Hashfunction | HMAC | A HMAC object, only HMACSHA256 and HMACSHA512 are valid options. | HMACSHA256 |
Testing is setup for Visual Studio, playlists are provided to reduce testing time rather than going through the full set, TestWorkFactor384 will significantly reduce time taken. Running the full test suite should take ~30 mins on an average cpu. The kats.txt file consists of 400 KDF and 2000 Makwa known answer tests.
-
This implementation enforces specific work factors of the form w = ζ · 2ᵟ, where ζ = 2 or 3, and δ ≥ 0. Some valid work factors: 256, 384, 512, 768, 1024, 1536, 2048, 3072, 4096, 6144, 8192, 12288, 16384
-
The final hash string doesn't differentiate between SHA-256 and SHA-512. If verifying from an unknown source test both algorithms.
-
A unique 2048-bit modulus is generated on first use and stored in the libraries folder as a binary file named modulus, generating your own is possible through either OpenSSL or the MakwaPrivateKey class as is testing for primality and correct type. Modulus must be a Blum integer which is the product of 2 primes p & q of the type: prime ≡ 3 (mod 4).
-
A standalone .dll is available here
-
The use of Pre and Post hashing affects certain features (delegation and fast-path are unaffected):