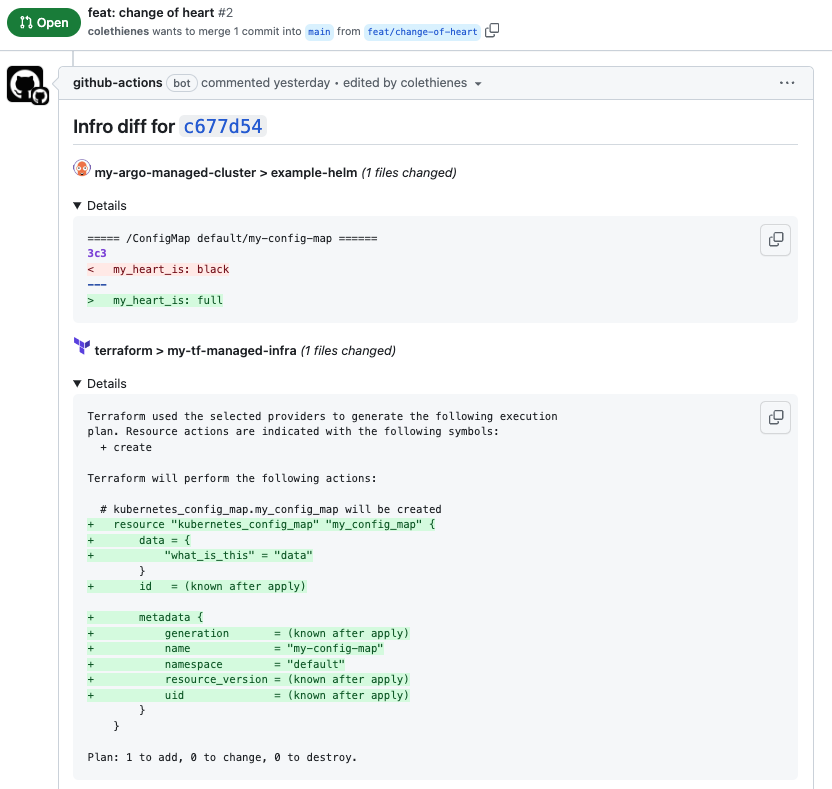
Infro is a GitOps tool which helps you understand how your changes will affect your infrastructure, before you merge. By integrating with different IaC providers, Infro provides a clear, holistic view of your changes on pull requests:
Infro supports running dry runs on different IaC providers and publishing results to pull requests for different version control systems:
| GitHub Action | Self-hosted | Infro Cloud | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argo CD diffs | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Terraform diffs | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 |
| AWS CDK diffs | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 |
| GitHub comments | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| GitLab comments | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 |
| No-code | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| PR Check status | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
Nearly all IaC tools provide an option to perform diffs and dry runs, but they usually rely on you manually running them. Many companies have created custom solutions to publish PR comments for their IaC of choice, but there hasn't yet been a generic solution.
| Infro doesn't require you to expose your infrastructure to the public internet or give third-party permissions. | One solution should be able to double check your changes across all your infra. Is your IaC or VCS not supported? It should be easy to integrate. |
| Infro doesn't rely on manually intervention to perform dry runs across different infrastructure. Just open a pull request, and let Infro take care of the rest. | You don't always need to see every changed line, just the ones that matter. Infro is on a mission to point out the changes that matter. |
Infro integrates with different version control systems (VCSs) and IaC providers (i.e. deployers). Infro detects when a new commit is added to a VCS pull request. Depending on the installation, this happens either by polling for changes or by an event trigger. Infro determines how the commit will change the live infrastructure by running a dry run against all of the IaC providers (i.e. deployers) defined in the configuration yaml, and comment the diffs back to the pull request.
Self-hosted deployments run in poll mode. Infro will continuously poll the VCS API (e.g. Github) to scan for new pull requests commits under the configured organization or user (i.e. owner). Therefore, you don't need to expose your infrastructure to a third-party.
Some deployments run in event-driven mode such as GitHub Actions and Infro Cloud. When a new commit is added to a pull request, Infro is triggered to perform dry runs for that revision.
Installing as a Github Action to have Infro comment diffs on each pull request in that repository. Add a job to your GitHub action yaml that is triggered when a pull_request is opened. Here's an example configuration for running diffs against an Argo CD cluster:
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
comment-diffs:
name: comment diffs
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
pull-requests: write
steps:
- uses: infro-io/comment-diffs-action@v1.4
with:
repo: ${{ github.repository }}
revision: ${{ github.sha }}
pull-number: ${{ github.event.number }}
config: |
deployers:
- type: argocd
name: my-argo-cluster
endpoint: ${{ secrets.ARGOCD_ENDPOINT }}
authtoken: ${{ secrets.ARGOCD_TOKEN }}
vcs:
type: github
authtoken: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}You can use the example-helm repo for reference.
The action requires pull-requests: write permissions to comment.
You must also pass the repo, revision, and pull-number from github context.
GITHUB_TOKEN is provided automatically, but you must provide additional secrets, such as ARGOCD_TOKEN, in repository secrets.
More information about the configuration here.
The self-hosted deployment polls the version control system for new pull requests and comments diffs on the ones it finds (more info).
Infro can be installed into your Kubernetes cluster by using kubectl or Kustomize.
First save the config file as a Kubernetes secret in infro-secrets.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: infro-secrets
data:
owner: <GITHUB_ORG_OR_USER>
config: |
deployers:
- type: argocd
name: my-cluster
endpoint: <ARGOCD_ENDPOINT>
authtoken: <ARGOCD_TOKEN>
vcs:
type: github
authtoken: <GITHUB_TOKEN>Then add them to the infro namespace:
kubectl create namespace infro
kubectl apply -n infro -f infro-secrets.yamlThen create the infro namespace and install the deployment:
kubectl apply -n infro -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/infro-io/infro-core/main/deploy/install.yamlor you can install it with Kustomize:
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: infro
resources:
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/infro-io/infro-core/main/deploy/install.yamlYou can also try this out locally by using Tilt.
Check out this repository and open the Tiltfile.
Replace the ARGOCD_ENDPOINT, ARGOCD_TOKEN, GITHUB_TOKEN, and GITHUB_OWNER values, then run:
tilt upThen open a pull request for a repository managed by your Argo CD and watch the magic happen. More information about the configuration here.
There is no code or deployment required if you choose to use Infro Cloud. All setup is performed in the UI at infro.io.
- Configure your organization https://infro.io/docs/configure-org
- Registering your Argo CD instance https://infro.io/docs/register-argo-cd
- The config yaml structure:
deployers:
- type: argocd
name: <ARBITRARY_NAME>
authtoken: <ARGOCD_TOKEN>
endpoint: <ARGOCD_ENDPOINT>
- type: terraform
workdir: <TERRAFORM_WORKDIR>
vcs:
type: github
authtoken: <GITHUB_TOKEN>endpoint: The Argo CD server address without the protocol (e.g.http). For example, the default endpoint in Kubernetes clusters should beargocd-server.argocd.svc.cluster.local.authtoken: an Argo CD automation token. See how to generate a secure token:
How to generate an Argo CD token
The account needs the apiKey capability in order to generate an auth token.
If you already have an account with this capability, you can skip this step.
The account can be added by modifying argocd-cm ConfigMap:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-cm
namespace: argocd
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-cm
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: argocd
data:
accounts.infro: "apiKey"The account also needs permissions to read applications and projects to perform app diff.
The account policy can be added by modifying argocd-rbac-cm ConfigMap:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-rbac-cm
namespace: argocd
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-rbac-cm
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: argocd
data:
policy.csv: |
p, role:readonly, applications, get, *, allow
p, role:readonly, projects, get, *, allow
g, infro, role:readonlyVisit your ArgoCD UI and go to Settings > Accounts. Under Tokens, click Generate New.
workdir: The Terraform working directory.
authtoken: a GitHub personal access token. See how to create one here.
All contributions are welcome!
Commands:
$ make help
build-docker: Build Docker image
build-go: Build go binary
format: Format code based on linter configuration
help: Show help for each of the Makefile recipes.
lint: Run linters
test-integration: Run integration tests
test-unit: Run unit tests