This is the soure code repository for my 2019 Computer Science Senior Thesis project at Willamette University. For my project I solicited and organized past Washington State Ferry departure data and other sources of information. The information was fed through an Amazon Alexa skill that provides future departure predictions and other helpful information for ferry riders.
In this README I try to be succinct while including more information in the Wiki Page for this repository.
When I started this project I had many different tools in mind that I wanted to use. The code I wrote in exploring these tools is included here but, ultimately, I ended up doing most everything with Amazon Web Services.
All Jupyter Notebooks were run through Anaconda with Python 3.6.2.
- In most of the files that interface with Amazon Web Services my bucket name is not included. I usually have a variable called
bucket_nameor something that in this public repository is redacted to just '#####'. If trying to replicate you will need to fill this in with your bucket name. - Within the python scripts and Jupyter notebooks most of the methods have docstrings. Look here at the README for info first, if you need more info see if there is a link to a corresponding wiki then if you need more info on a specific method look for the docstring.
- The AWS servers were on Greenwich Mean Time so I had to subtract 7 hours from that time to get Pacific time (on daylight savings time). This will obviously change depending on weather or not daylight savings time is active.
Hopefully I can provide some instruction on where to start if you are looking at my project for the first time and want to understand it.
- Get a feel for the data. Due to the size I did not include all the data that WSDOT sent me. You can do a public records request and also see a preview of the data I worked with on this wiki page.
- Look at this wiki page to gain a understanding of the Alexa Skill intent I have.
- Look at the
lambda-functionsdirectory and get a feel for what they are doing. - Feel free to explore from there! Be sure to look at the description of directories below as you are exploring.
| directory | description | dependencies |
|---|---|---|
| ARIMA | Contains a Jupyter Notebook with code I used to try and fit an ARIMA model to my data. This was never used in the final product. | 'pandas', 'matplotlib', 'statsmodels' |
| AWS-Sagemaker | Contains Jupyter Notebooks that were run in the cloud on AWS SageMaker. See my AWS-SageMaker wiki page for more information on each notebook. | AWS SageMaker |
| Exploratory-Data-Analysis | Contains Jupyter Notebooks that I ran locally on my PC to start getting a feel for the data I had recieved from WSDOT. See the wiki page for more info. | 'pandas', 'numpy' |
| Facebook-Prophet | Contains a Jupyter Notebook with code that I used to fit a Facebook Prophet model. | 'pandas', 'fbprophet' |
| Realtime-Departure-Collection | Contians a python script that runs in a infinite loop and collects live departure data from the WSDOT Vessels API and saves it to AWS S3. | 'numpy', 'pandas' |
| Retrieve-Schedule | Contains a python script that invokes the WSDOT Schedules API and writes out a JSON file that is used by a lambda function to respond with future departures. See the Retrieve Schedule wiki page for more info. | |
| Turning-Data-into-Time-Series | Contains two Jupyter notebooks. One of them was used to create timestamps for Bainbridge departures and the other one is used to calculate seconds late/early. Timestamps with seconds late/early is what I used to train my model. More info on this wiki page. | 'pandas', 'numpy' |
| csv-files | This is where I saved the csv files after doing things like generating timestamps, calculating seconds late, and linearily interpolating the data. I seperated out some of the steps into different folders then there is a Jupyter notebook with code I used to manage the files in the folder. | 'pandas' |
| docs | Saving things needed for the documentation of this project. | |
| lambda-functions | This is the code for the python AWS Lambda functions that serve my Alexa Skill. More info on each function on this wiki page. | Need to be run as AWS Lambda functions, AWS CLI required to sync locally to AWS Lambda. |
- Get the data from WSDOT.
- Use the code in the
Turning-Date-Into-Time-Seriesdirectory to add timestamps and make the data have a consistent 5-minute interval. Upload the data to S3 as a csv. My master csv file is csv_files/Bainbridge_Departures_Master.csv - Use the code in the
Retrieve-Scheduledirectory to make a JSON file with the current schedule. Upload this file to S3. - Upload the Jupyter Notebook
AWS-SageMaker/DeepAR_AE.ipynbto AWS SageMaker and create a model and deploy it to an endpoint. (Sounds hard but AWS makes that all easy). - Create lambda functions in AWS Lambda for each lambda function in the lambda-function folder. Be sure to set the correct permissions using AWS IAM (look up online how to do it).
- Create each of the four intents mentioned above in the Alexa Skills Kit. Make sure the Alexa Skills Kit is connected to the ferry-skill lambda function. The YouTube video in the footnote above shows how to do this.
- Set up the script in the Realtime-Departure-Collection direction to run and collect the proper data.
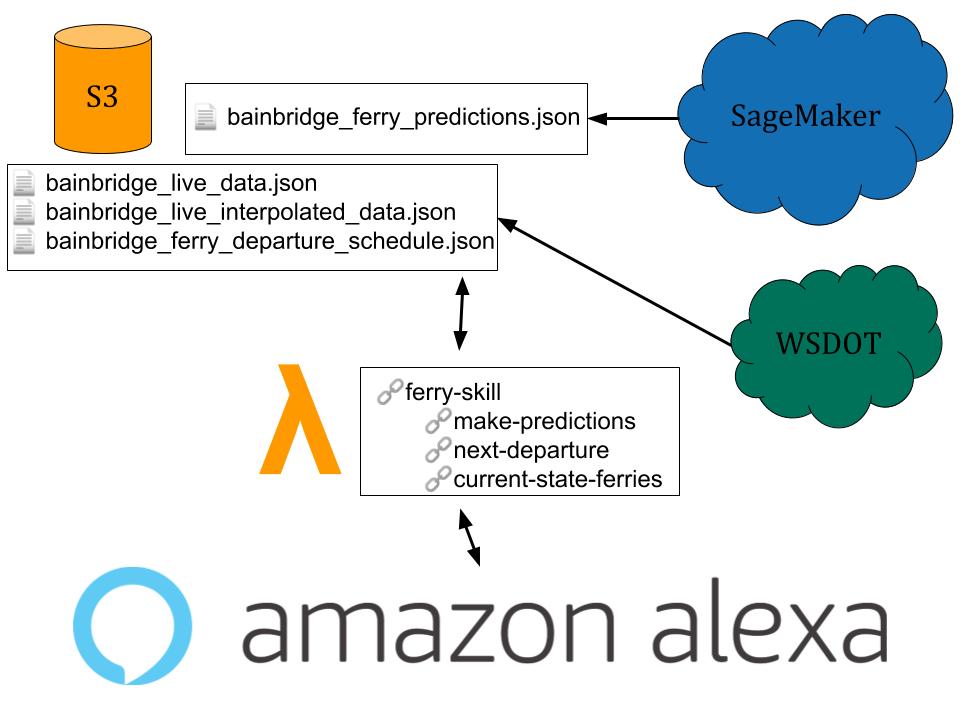
Here is a basic diagram showing how things are organized into the Alexa Skill:
More explanation about this diagram can be found on this wiki page.