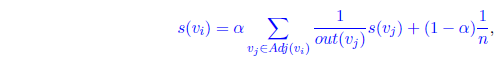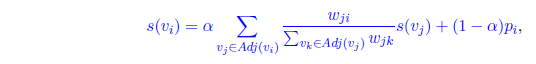The goal of this project is to use PageRank to derive a ranking of words in a document based on their PageRank scores. The PageRank score of a word serves as an indicator of the importance of the word in the text. Also compare the MRR of the above PageRank algorithm with the MRR of a ranking of words based on their TF-IDF ranking scheme.
The project name is: HW2_PageRank and it was created using the Eclipse IDE. The program solves all the questions in a single execution (run).
For point 1, a directed graph was used (using a hash table and adjacency lists as data structures). For point 2 and 2', a function was created that returns the PageRank scores per word by document. For point 3, a parameterized function was created that generates both unigrams and n-grams. For point 4, a function was created that calculates the MRR from a list of proposed n-grams and the phrases available in the gold-standard files. For point 5, a function was created that calculates the TF-IDF scores for each word of each abstract document and then calculates the MRR score to the proposed n-grams.
For this project, it was used the WWW collection consisting of titles and abstracts of research articles published in the WWW conference.
- Simple PageRank: run PageRank on each word graph corresponding to each document in the collection as
follows:
- Initialization: s = [s(V1), . . . , s(Vn)] = [1/n, . . . , 1/n], where n = |V|.
- Score nodes in a graph using their PageRank obtained by iteratively computing the equation.
- Where α is a damping factor (α = 0.85) and p = [1/n, . . . , 1/n].
- Weighted PageRank: assume the weight Wij of an edge (Vi, Vj) is calculated as the number of times the corresponding words Wi and Wj are adjacent in text. Run PageRank on each word graph corresponding to each document in the collection using:
- Mean reciprocal rank (MRR): Rd is the rank at which the first correct prediction was found for d ∈ D.
- Java (JDK 1.7)
- Eclipse IDE
- Page Rank
- TF-IDF
- Tokenization
- Stemming
- Lemmatization
- Remove stop-words
The project has an executable in the 'jar' folder. The JAR name is: KD_HW2_v1.7.jar and you must send the path of the "data/www/" directory as a parameter, the n-grams size and the comparison type as parameters.
Therefore, to run the program you should go into the jar directory on your machine and then execute the following command:
cd jar_folder
java -jar KD_HW2_v1.7.jar data/ [UNIGRAMS|NGRAMS] [DIRECT|BY_TOKENS]
Execution examples:
cd jar_folder
java -jar KD_HW2_v1.7.jar data/ UNIGRAMS DIRECT
java -jar KD_HW2_v1.7.jar data/ UNIGRAMS BY_TOKENS
java -jar KD_HW2_v1.7.jar data/ NGRAMS DIRECT (DEFAULT CONFIGURATION)
java -jar KD_HW2_v1.7.jar data/ NGRAMS BY_TOKENS
The .JAR program must be run with Java 7 or higher.
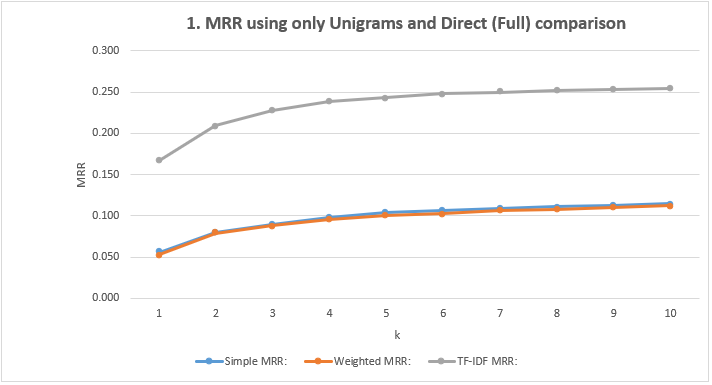
- Show the MRR Scores: Using only Unigrams and Direct (Full) comparison
| k=1 | k=2 | k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | k=7 | k=8 | k=9 | k=10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple MRR | 0.056 | 0.080 | 0.090 | 0.098 | 0.104 | 0.106 | 0.109 | 0.111 | 0.113 | 0.115 |
| Weighted MRR | 0.053 | 0.079 | 0.088 | 0.096 | 0.101 | 0.103 | 0.106 | 0.108 | 0.110 | 0.112 |
| TF-IDF MRR | 0.167 | 0.209 | 0.228 | 0.239 | 0.243 | 0.248 | 0.250 | 0.252 | 0.253 | 0.254 |
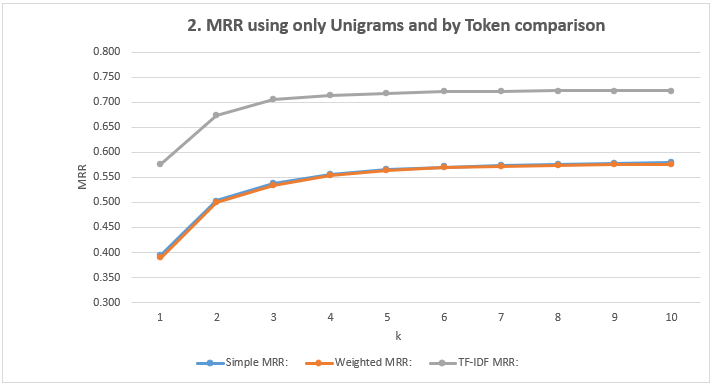
- Show the MRR Scores: Using only Unigrams and comparison by Token
| k=1 | k=2 | k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | k=7 | k=8 | k=9 | k=10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple MRR | 0.394 | 0.503 | 0.537 | 0.556 | 0.566 | 0.570 | 0.574 | 0.576 | 0.577 | 0.579 |
| Weighted MRR | 0.388 | 0.500 | 0.534 | 0.554 | 0.564 | 0.569 | 0.572 | 0.574 | 0.575 | 0.576 |
| TF-IDF MRR | 0.576 | 0.674 | 0.706 | 0.714 | 0.718 | 0.721 | 0.722 | 0.723 | 0.723 | 0.723 |
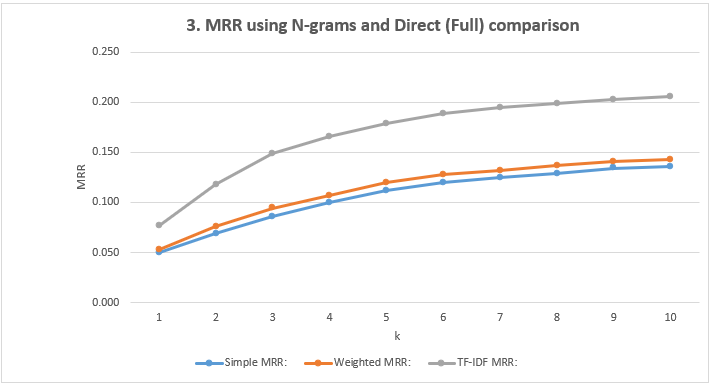
- Show the MRR Scores: Using N-grams and Direct (Full) comparison
| k=1 | k=2 | k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | k=7 | k=8 | k=9 | k=10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple MRR | 0.050 | 0.069 | 0.086 | 0.100 | 0.112 | 0.120 | 0.125 | 0.129 | 0.134 | 0.136 |
| Weighted MRR | 0.053 | 0.076 | 0.094 | 0.107 | 0.120 | 0.128 | 0.132 | 0.137 | 0.141 | 0.143 |
| TF-IDF MRR | 0.077 | 0.118 | 0.149 | 0.166 | 0.179 | 0.189 | 0.195 | 0.199 | 0.203 | 0.206 |
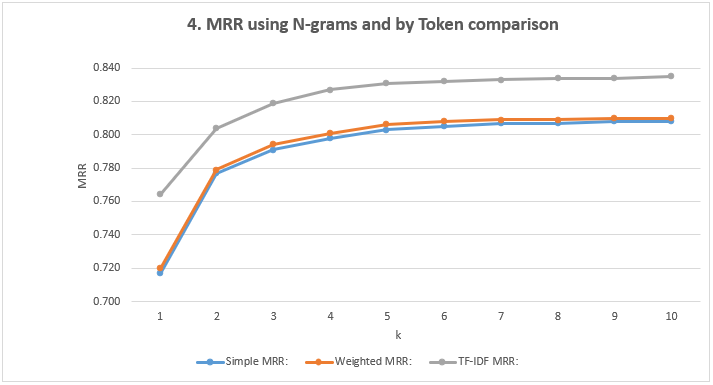
- Show the MRR Scores: Using N-grams and comparison by Token
| k=1 | k=2 | k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | k=7 | k=8 | k=9 | k=10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple MRR | 0.717 | 0.777 | 0.791 | 0.798 | 0.803 | 0.805 | 0.807 | 0.807 | 0.808 | 0.808 |
| Weighted MRR | 0.720 | 0.779 | 0.794 | 0.801 | 0.806 | 0.808 | 0.809 | 0.809 | 0.810 | 0.810 |
| TF-IDF MRR | 0.764 | 0.804 | 0.819 | 0.827 | 0.831 | 0.832 | 0.833 | 0.834 | 0.834 | 0.835 |
- The results between the simple and the weighted PageRank are practically the same. This may be due to the fact that the graphs weights are mostly low.
- The results of TF-IDF were always better than those obtained by PageRanks.
- The way in which the n-grams are created (unigrams, bigrams or trigrams) and the way in which they compare with the exits of the gold-standard files (directly or by tokens) have a marked influence on the results of the MRR.
- Created By: Andres Segura Tinoco
- Created On: June 27, 2018
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.