| layout | menu | title | permalink |
|---|---|---|---|
docs |
docs |
Scale |
/docs/scale.html |
Scales are functions that transform a domain of data values (numbers, dates, strings, etc.) to a range of visual values (pixels, colors, sizes). Internally, Vega-Lite uses Vega scales, which are derived from the d3-scale library. For more background about scales, please see "Introducing d3-scale" by Mike Bostock.
Vega-Lite automatically creates scales for fields that are mapped to position and mark property channels. To customize the scale of a field, users can provide a scale object as a part of the field definition to customize scale properties (e.g., type, domain, and range).
// A Single View or a Layer Specification
{
...,
"mark/layer": ...,
"encoding": {
"x": {
"field": ...,
"type": ...,
"scale": { // scale
"type": ...,
...
},
...
},
"y": ...,
...
},
...
}Besides the scale property of each encoding channel, the top-level configuration object (config) also provides scale config (config: {scale: {...}}) for setting default scale properties for all scales.
For more information about guides that visualize the scales, please see the axes and legends pages.
{:.no_toc}
- TOC {:toc}
{:#type}
The type property can be specified to customize the scale type.
{% include table.html props="type" source="Scale" %}
By default, Vega-Lite use the following scale types for the following data types and encoding channels:
| Nominal / Ordinal | Quantitative | Bin-Quantitative1 | Temporal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X, Y | Band / Point2 | Linear | Linear | Time |
| Size, Opacity | Point | Linear | Linear | Time |
| Color | Ordinal | Linear | Bin-Ordinal | Linear |
| Shape | Ordinal | N/A | N/A | N/A |
{:#domain}
By default, a scale in Vega-Lite draws domain values directly from a channel's encoded field. Users can specify the domain property of a scale to customize its domain values. To sort the order of the domain of the encoded, the sort property of a field definition can be specified.
{% include table.html props="domain,domainMax,domainMin,domainMid" source="Scale" %}
A common use case for the domain property is to limit, for example, the x range of values to include in a plot. However, setting the domain property alone is insufficient to achieve the desired effect.
For a time scale, we can set scale domain to an array datetime objects, as shown below.
For example, consider the line plot specification below in which the x domain is restricted to the range [300, 450].
There are two approaches to keep the mark from being plotted outside the desired x range of values.
-
The first one is to set
clip: truein mark definition. -
The second approach is to use
transform. Note that these two approaches have slightly different behaviors. Usingtransformremoves unwanted data points, yet settingcliptotrueclips the mark to be the enclosing group's width and height.
{:#range}
The range of the scale represents the set of output visual values. Vega-Lite automatically determines the default range for each encoding channel using the following rules:
| Channels | Default Range |
|---|---|
x |
The range is by default [0, width]. |
y |
The range is by default [0, height]. |
opacity |
Derived from the scale config's min/maxOpacity. |
color |
Derived from the following named ranges based on the field's type: • "category" for nominal fields. • "ordinal" for ordinal fields. • "heatmap" for quantitative and temporal fields with "rect" marks and "ramp' for other marks. See the color scheme section for examples. |
size |
Derived from the following named ranges based on the mark type: • min/maxBandSize for bar and tick. • min/maxStrokeWidth for line and rule. • min/maxSize for point, square, and circle • min/maxFontSize for text |
shape |
Derived from the pre-defined named range "symbol". |
To customize range values, users can directly specify range or specify the special scheme property for ordinal and continuous color scales.
{% include table.html props="range,rangeMin,rangeMax" source="Scale" %}
In this example, we create a scale that maps the field "l" to colors specified in the field "c":
Note: This only works if there is a 1:1 mapping between the color domain field (l) and therange field (c).
We may use rangeMin if we want to override just the minimum value of the range, while keeping the default maximum value of the range.
Similarly, we may use rangeMax if we want to override just the maximum value of the range, while keeping the default minimum value of the range.
{:#scheme}
Color schemes provide a set of named color palettes as a scale range for the color channel. Vega-Lite (via Vega) provides a collection of perceptually-motivated color schemes, many of which are drawn from the d3-scale, d3-scale-chromatic, and ColorBrewer projects.
By default, Vega-Lite assigns different default color schemes based on the types of the encoded fields:
- Nominal fields use the
"categorical"pre-defined named range (the"tableau10"scheme by default).
- Ordinal fields use the
"ordinal"pre-defined named color range (the"blues"color scheme by default).
- Quantitative and temporal fields use the pre-defined named color range
"heatmap"(the"viridis"scheme by default) for rect marks and"ramp"(the"blues"scheme by default) for other marks.
There are multiple ways to customize the scale range for the color encoding channel:
{% include table.html props="scheme" source="Scale" %}
You can customize the scheme by referencing an existing color scheme. For example, the following plot uses the "category20b" scheme.
{:#scheme-params}
The scheme property can also be a scheme parameter object, which contain the following properties:
{% include table.html props="name,extent,count" source="SchemeParams" %}
See the range config documentation for details.
{:#continuous}
In addition to type, domain, and range, all scales share the following properties:
{% include table.html props="reverse,round" source="Scale" %}
Continuous scales map a continuous domain (numbers or dates) to a continuous output range (pixel locations, sizes, colors). Supported continuous scale types for quantitative fields are "linear", "log", "pow", "sqrt", and "symlog". Meanwhile, supported continuous scale types for temporal fields are "time", "utc", and "symlog".
By default, Vega-Lite uses "linear" scales for quantitative fields and uses "time" scales for temporal fields for all encoding channels.
In addition to type, domain, and range, continuous scales support the following properties:
{% include table.html props="clamp,interpolate,nice,padding,zero" source="Scale" %}
{:#linear}
Linear scales ("linear") are quantitative scales scales that preserve proportional differences. Each range value y can be expressed as a linear function of the domain value x: y = mx + b.
{:#pow}
Power scales ("pow") are quantitative scales scales that apply an exponential transform to the input domain value before the output range value is computed. Each range value y can be expressed as a polynomial function of the domain value x: y = mx^k + b, where k is the exponent value. Power scales also support negative domain values, in which case the input value and the resulting output value are multiplied by -1.
{% include table.html props="exponent" source="Scale" %}
{:#sqrt}
Square root ("sqrt") scales are a convenient shorthand for power scales with an exponent of 0.5, indicating a square root transform.
{:#log}
Log scales ("log") are quantitative scales in which a logarithmic transform is applied to the input domain value before the output range value is computed. Log scales are particularly useful for plotting data that varies over multiple orders of magnitude. The mapping to the range value y can be expressed as a logarithmic function of the domain value x: y = m loga(x) + b, where a is the logarithmic base.
As log(0) = -∞, a log scale domain must be strictly-positive or strictly-negative; the domain must not include or cross zero. A log scale with a positive domain has a well-defined behavior for positive values, and a log scale with a negative domain has a well-defined behavior for negative values. (For a negative domain, input and output values are implicitly multiplied by -1.) The behavior of the scale is undefined if you run a negative value through a log scale with a positive domain or vice versa.
{% include table.html props="base" source="Scale" %}
Example: The following plot has a logarithmic y-scale.
{:#symlog}
Symmetric log scales (symlog) are quantitative scales scales that provide scaling similar to log scales, but supports non-positive numbers. Symlog scales are particularly useful for plotting data that varies over multiple orders of magnitude but includes negative- or zero-valued data. For more, see "A bi-symmetric log transformation for wide-range data" by Webber for more.
{% include table.html props="constant" source="Scale" %}
{:#time}
Time and UTC scales ("time" and "utc") are continuous scales with a temporal domain: values in the input domain are assumed to be Date objects or timestamps. Time scales use the current local timezone setting. UTC scales instead use Coordinated Universal Time.
{:#piecewise}
We can use any types of continuous scales ("linear", "pow", "sqrt", "log", "symlog", "time", "utc" to create a diverging color graph by specifying a custom domain with multiple elements.
If range is specified, the number of elements in range should match with the number of elements in domain. Diverging color schemes are also useful as a range for a piecewise scale.
Example
{:#discrete}
Discrete scales map values from a discrete domain to a discrete or continuous range.
{:#ordinal}
Ordinal scales ("ordinal") have a discrete domain and range. These scales function as a “lookup table” from a domain value to a range value.
By default, Vega-Lite automatically creates ordinal scales for color and shape channels. For example, the following plot implicitly has two ordinal scales, which map the values of the field "Origin" to a set of colors and a set of shapes.
The range of an ordinal scale can be an array of desired output values, which are directly mapped to elements in the domain. Both domain and range array can be re-ordered to specify the order and mapping between the domain and the output range. For ordinal color scales, a custom scheme can be set as well.
{:#band}
Band and point scales accept a discrete domain similar to ordinal scales, but map this domain to a continuous, numeric output range such as pixels.
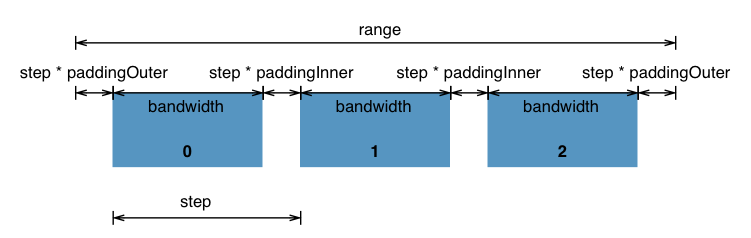
Band scales ("band") compute the discrete output values by dividing the continuous range into uniform bands. Band scales are typically used for bar charts with an ordinal or categorical dimension.
In addition to a standard numerical range value (such as [0, 500]), band scales can be given a fixed step size for each band. The actual range is then determined by both the step size and the cardinality (element count) of the input domain.
This image from the d3-scale documentation illustrates how a band scale works:
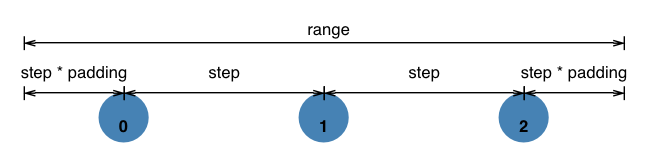
Point scales ("point") are a variant of band scales where the internal band width is fixed to zero. Point scales are typically used for scatterplots with an ordinal or categorical dimension. Similar to band scales, point scale range values may be specified using either a numerical extent ([0, 500]) or a step size ({"step": 20}).
This image from the d3-scale documentation illustrates how a point scale works:
By default, Vega-Lite uses band scales for nominal and ordinal fields on position channels (x and y) of bar or rect marks. For x and y of other marks and size and opacity, Vega-Lite uses point scales by default.
For example, the following bar chart has uses a band scale for its x-position.
{:#range-step}
To customize the step size of band scales for x/y-fields, we can set the step property of the view's width/height.
For example, we can either make a bar chart have a fixed width:
or set the width per discrete step:
To customize the range of band and point scales, users can provide the following properties:
{% include table.html props="align,padding,paddingInner,paddingOuter" source="Scale" %}
{:#discretizing}
Discretizing scales break up a continuous domain into discrete segments, and then map values in each segment to a range value.
{:#bin-linear}
Binned linear scales ("bin-linear") are a special type of linear scale for use with binned fields to correctly create legend labels. Vega-Lite always uses binned linear scales with binned quantitative fields on size and opacity channels.
For example, the following plot has a binned field on the size channel.
{:#bin-ordinal}
Binned ordinal scales ("bin-ordinal") are a special type of ordinal scale for use with binned fields to correctly create legend labels. Vega-Lite always uses binned ordinal scales with binned quantitative fields on the color channel.
For example, the following plot has a binned field on the color channel.
Similar to ordinal color scales, a custom range or scheme can be specified for binned ordinal scales.
In addition, bins property can be used to specify bin boundaries over the scale domain.
{% include table.html props="bins" source="Scale" %}
{:#bins}
The bin specification object for the scale bins properties support the following properties:
{% include table.html props="bins" source="ScaleBinParams" %}
{:#quantile}
Quantile scales ("quantile") map a sample of input domain values to a discrete range based on computed quantile boundaries. The domain is considered continuous and thus the scale will accept any reasonable input value; however, the domain is specified as a discrete set of sample values. The number of values in (i.e., the cardinality of) the output range determines the number of quantiles that will be computed from the domain. To compute the quantiles, the domain is sorted, and treated as a population of discrete values. The resulting quantile boundaries segment the domain into groups with roughly equals numbers of sample points per group. If the range is not specified, the domain will be segmented into 4 quantiles (quartiles) by default.
Quantile scales are particularly useful for creating color or size encodings with a fixed number of output values. Using a discrete set of encoding levels (typically between 5-9 colors or sizes) sometimes supports more accurate perceptual comparison than a continuous range. For related functionality see quantize scales, which partition the domain into uniform domain extents, rather than groups with equal element counts. Quantile scales have the benefit of evenly distributing data points to encoded values. In contrast, quantize scales uniformly segment the input domain and provide no guarantee on how data points will be distributed among the output visual values.
{:#quantize}
Quantize scales ("quantize") are similar to linear scales, except they use a discrete rather than continuous range. The quantize scale maps continuous value to a discrete range by dividing the domain into uniform segments based on the number of values in (i.e., the cardinality of) the output range. Each range value y can be expressed as a quantized linear function of the domain value x: y = m round(x) + b. If the range property is not specified, the domain will be divided into 4 uniform segments by default.
Quantize scales are particularly useful for creating color or size encodings with a fixed number of output values. Using a discrete set of encoding levels (typically between 5-9 colors or sizes) sometimes supports more accurate perceptual comparison than a continuous range. For related functionality see quantile scales, which partition the domain into groups with equal element counts, rather than uniform domain extents.
{% include table.html props="nice,zero" source="Scale" %}
{:#threshold}
Threshold scales ("threshold") are similar to quantize scales, except they allow mapping of arbitrary subsets of the domain (not uniform segments) to discrete values in the range. The input domain is still continuous, and divided into slices based on a set of threshold values provided to the required domain property. The range property must have N+1 elements, where N is the number of threshold boundaries provided in the domain.
{:#disable}
To directly encode the data value, the scale property can be set to null.
For example, the follow bar chart directly encodes color names in the data.
{:#config}
// Top-level View Specification
{
...
"config": {
"scale": {
... // Scale Config
},
"range": {
... // Scale Range Config
},
...
}
...
}To provide themes for all scales, the scale config (config: {scale: {...}}) can contain the following properties:
{% include table.html props="bandPaddingInner,barBandPaddingInner,rectBandPaddingInner,bandWithNestedOffsetPaddingInner,offsetBandPaddingInner,bandPaddingOuter,bandWithNestedOffsetPaddingOuter,offsetBandPaddingOuter,continuousPadding,pointPadding" source="ScaleConfig" %}
{% include table.html props="maxBandSize,minBandSize,maxFontSize,minFontSize,maxOpacity,minOpacity,maxSize,minSize,maxStrokeWidth,minStrokeWidth" source="ScaleConfig" %}
{% include table.html props="clamp,round,xReverse,useUnaggregatedDomain,zero" source="ScaleConfig" %}
{:#range-config}
The scale range configuration (config: {range: {...}}) defines key-value mapping for named scale ranges: the keys represent the range names, while the values define valid range or, for named color ranges, Vega scheme definitions.
By default, Vega-Lite (via Vega) includes the following pre-defined named ranges:
{% include table.html props="category,diverging,heatmap,ordinal,ramp,symbol" source="RangeConfig" %}
See this file for the default values of named ranges.