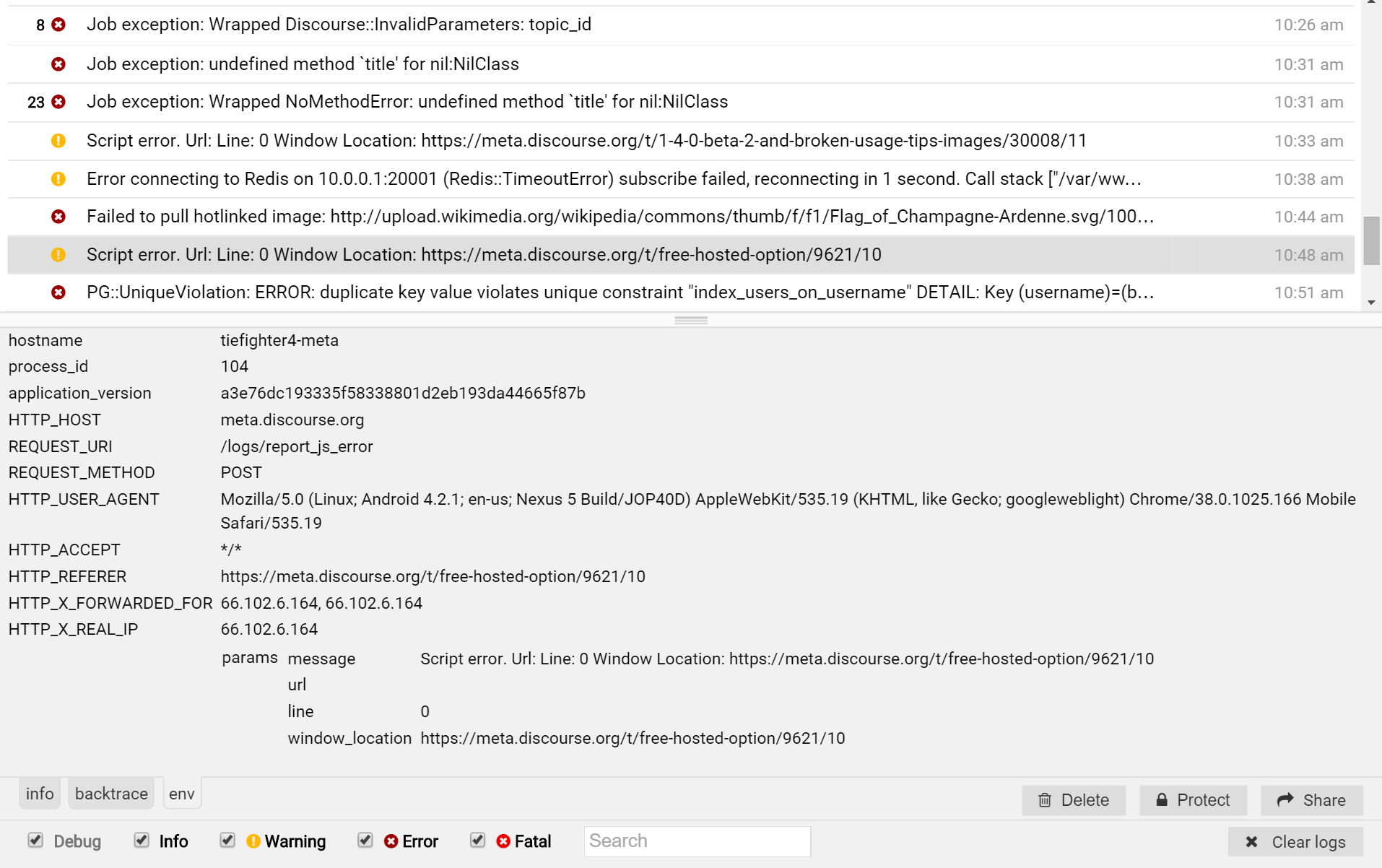
Logster is an embedded Ruby "exception reporting service" admins can view on live websites, at http://example.com/logs
Play with a live demo at logster.info/logs.
Add these lines to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'redis'
gem 'logster'
And then execute:
$ bundle
Make logster web available add the following to your routes.rb:
constraints lambda { |req| req.session["admin"] } do
mount Logster::Web => "/logs"
end
By default, logster will only run in development and production environments.
To run logster in other environments, in config/application.rb
Logster.set_environments([:development, :staging, :production])
Logster can be configured using Logster.config:
Logster.config.application_version: set to a unique identifier denoting version of your app. The "solve" function takes this version into account when suppressing errors.Logster.config.enable_js_error_reporting: enable js error reporting from clientsLogster.config.rate_limit_error_reporting: controls automatic 1 minute rate limiting for JS error reporting.Logster.config.web_title:<title>tag for logster error page.Logster.config.enable_custom_patterns_via_ui: enable the settings page (/settings) where you can add suppression and grouping patterns.Logster.config.maximum_message_size_bytes: specify a size in bytes that a message cannot exceed. Note this isn't 100% accurate, meaning a message may still grow above the limit, but it shouldn't grow by more than, say, 2000 bytes.Logster.config.project_directories: This should be an array of hashes that map paths on the local filesystem to GitHub repository URLs. If this feature is enabled, Logster will parse backtraces and try to construct a GitHub URL to the exact file and line number for each line in the backtrace. For a Rails app, the config may look like this:Logster.config.project_directories = [{ path: Rails.root.to_s, url: "https://github.com/<your_org>/<your_repo>" }]. The GitHub links that are constructed will use themasterbranch. If you want Logster to use theapplication_versionattribute from theenvtab so that the GitHub links point to the exact version of the app when the log message is created, addmain_app: truekey to the hash.Logster.config.enable_backtrace_links: Enable/disable the backtrace links feature.Logster.config.gems_dir: The value of this config isGem.dir + "/gems/"by default. You probably don't need to change this config, but it's available in case your app gems are installed in a different directory. An example where this config is needed is Logster demo site: https://github.com/discourse/logster/blob/master/website/sample.rb#L77.
Logster allows you to register a callback when the rate of errors has exceeded a given limit.
Tracking buckets available are one minute and an hour.
Example:
Logster.register_rate_limit_per_minute(Logger::WARN, 60) do |rate|
puts "O no! The error rate is now #{rate} errors/min"
end
Logster.register_rate_limit_per_hour([Logger::WARN, Logger::ERROR, Logger::FATAL], 60) do |rate|
puts "O no! The error rate is now #{rate} errors/hour"
end
If you are seeing the error No such middleware to insert before: ActionDispatch::DebugExceptions after installing logster,
then you are using a conflicting gem like better_errors or web-console.
To avoid this error, make sure logster is added behind those conflicting gems in your Gemfile.
If you're using Logster with a non-rails app, you'll need to be careful that the env hashes of messages that Logster receives don't contain strings with invalid encoding because at some point Logster calls #to_json on the message env and the method will fail with JSON::GeneratorError.
The reason this doesn't happen in rails apps is because ActiveSupport has a monkey patch for #to_json.
admin_constraint = lambda do |request|
request.env['warden'].authenticate? and request.env['warden'].user.admin?
end
constraints admin_constraint do
mount Logster::Web, at: "/logs"
end
Out of the box, logster will use the default redis connection, to customise, in config/application.rb
Logster.store = Logster::RedisStore.new(redis_connection)
In case you may be using the rails_12factor gem in a production deployment on Heroku, the standard Rails.logger will not cooperate properly with Logster. Extend Rails.logger in your config/application.rb or config/initializers/logster.rb with:
if Rails.env.production?
Rails.logger.extend(ActiveSupport::Logger.broadcast(Logster.logger))
end
Logster UI is built using Ember.js
- Fork it ( https://github.com/discourse/logster/fork )
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b my-new-feature) - Run
cd client-app && npm install - Run
bundle exec rake client_devto start Sinatra server (port 9292) and Ember server (port 4200). Use Ember server for hot reload for client code. - Once you're done making changes, run
./build_client_app.shto make and copy a production build to the assets folder. - Commit your changes (
git commit -am 'Add some feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin my-new-feature) - Create a new Pull Request