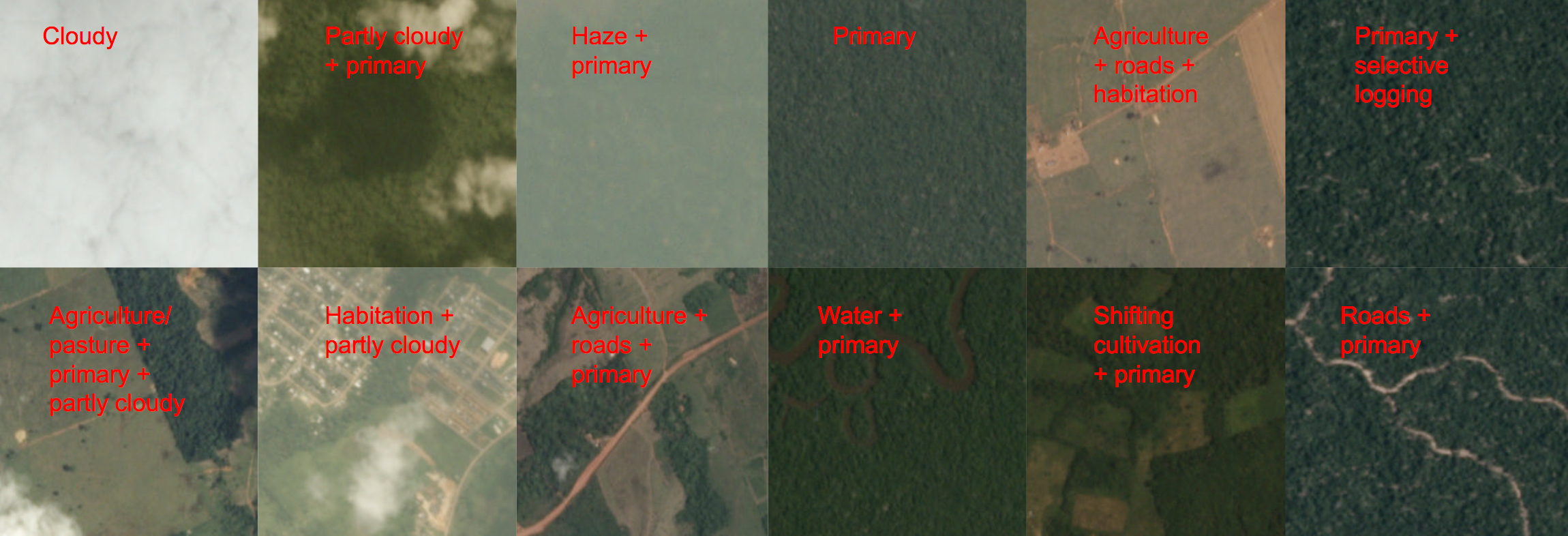
In order to tackle the global challenge of rapid deforestation, we use satellite imagery to understand land use patterns and atmospheric conditions. In this project, we apply machine learning algorithms and techniques for performing automated multi-label classification of satellite images of the Amazon basin using a dataset provided by Planet Labs, which is hosting a Kaggle competition for this task.
Multi-output satellite image classification refers to the task of classifying different features in satellite images into multiple categories simultaneously. Instead of predicting a single output class for an image, a multi-output classification model can predict several output classes, which can include features such as land cover, vegetation, and water bodies. This type of classification requires a model that can handle multiple outputs and incorporate dependencies between them. The model needs to be trained on a labeled dataset, which includes multiple annotated classes for each input image. Once trained, the model can be used to classify new satellite images into multiple output classes simultaneously. This can be particularly useful for applications such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response.
We employed different approaches with varying degrees of success in our endeavors to tackle the problem:
Model Explorationwherein we explore different online classification approaches such as the Passive-Aggressive Classifier approach as well as different dimensionality reduction techniques such as Incremental PCA, Mini-Batch K-Means as well as Online Dictionary Learning. We experiment with both the raw image data as well as their respective Histogram Of Gradients (HOG) features.Transfer Learningwherein we employ an 18-layer deep ResNet architecture in order to efficiently model the data. We experiment with different per-class thresholds on the validation set and evaluate our model on the test data set.CNNwherein we explore different CNN architectures using both Keras and PyTorch whilst expeimenting with optimization finetuning techniques such as data augmentation, SGD Nesterov momentum theory etc.